Overview
What is GIS?
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all types of data (spatial and non-spatial). GIS connects data to a map, integrating location data (where things are) with all types of descriptive information (what things are like there). This provides a foundation for mapping and analysis that is used in science and almost every industry. GIS helps users understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context. The benefits include improved communication, efficiency, better data management and informed decision making. (ESRI 2022 www.esri.com)
How does GIS Work?
GIS technology applies geographic science with tools for understanding and collaboration. It helps people reach a common goal: to gain actionable intelligence from all types of data. (ESRI 2022)
These systems are not just the software and hardware, but also, the collection of information (within a database) with where geographic features are located in your community. Building these various databases involves compiling the information from existing maps, field mapping projects, orthophoto imagery, anecdotal experiences or existing computer databases. A GIS database amalgamates all this geographic information so that it can be used together typically on a personal computer (PC), mobile device or online.
A working GIS integrates five key components: hardware, software, data, people, and methods/applications. Benefits of using a GIS include; Improved decision making, reduced operational costs, Enhanced communication and effective recording of geographical data.
What can you do with a Geographic Information System (GIS)?
A GIS is not simply a computer system or program for generating maps. In fact, a map is simply the most common way of reporting information from various GIS databases. GIS is used in Freeport, Grand Bahama for the following: Land Inventory Management, Parcel Fabric Management, Hurricane Assessments, Land Zone/Use & Urban Planning, Drone Mapping, Environmental Assessments, City Management Asset Management and Web Mapping.
Can I see an example of a GIS Map?
The GBPA GIS Public Parcel Viewer shows all of Freeport’s Subdivisions and can assist residents with learning their correct Lot, Block, Unit or Tract information.
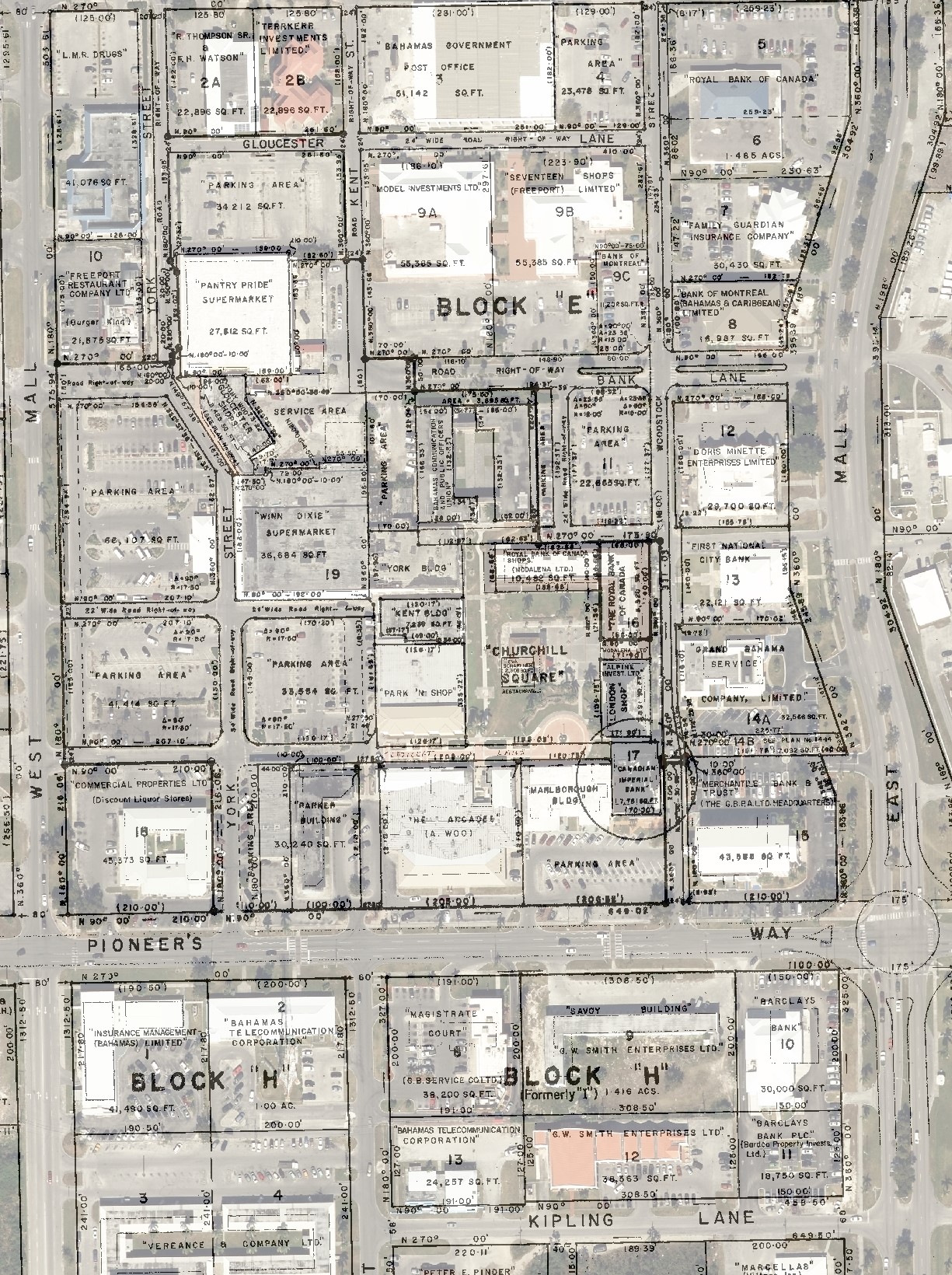
GIS Department Services
- Printed Survey Plat Maps (once available) Cost $ 10 Per Plat Map Excluding Research Cost if Applicable (11” x 17”)
- Printed Overlay Maps (survey plat map into 2021 aerial imagery) Cost $ 20 Per Overlay (11” x 17”)
- Provision of 20cm Resolution 1km x 1km Digital Tiles of Grand Bahama Island ($200 Per Tile)
- Provision of GIS shapefile Elevation 1km x 1km Digital Tiles of Grand Bahama Island ($ 200 Per Tile)
- Provision of GIS shapefile LiDAR 1km x 1km Digital Tiles of Grand Bahama Island ($ 200 Per Tile)
- See GIS Map showing Extent of Tiles and Tile IDs https://bit.ly/2021GBI_Tiles or https://arcg.is/0LXnG1
- Plotting of Architectural Plans (once available) Cost $ 10 Per Sheet or $ 15 Per Specific Sheet (24” x 36”) (Proof of Ownership is Compulsory) (Digital Copies are $ 5 Additional Per Sheet)
- Provision of Plotted Flood Hazard Maps (Freeport) Cost $ 30 Plain Paper and $ 45 Gloss Paper (24” x 36”)
- GIS Consultation Cost $ 100 Per Hour (service upon request)
- Various GIS Data of Grand Bahama (upon service request)
- Drone Mapping (Coming Soon!) Cost $ 100 Per Hour (service upon request)

